Comprehensive Care
Whether you are seeking relief from back pain, neck pain, headaches, or other musculoskeletal issues, we offer a comprehensive range of services to address various conditions. Our services are designed to promote overall well-being and improve your quality of life.
Personalized Approach
We recognize that each patient's journey to health is unique. That's why we take the time to listen to your concerns, understand your health history, and conduct thorough evaluations before developing a personalized treatment plan.
Holistic Wellness
At Exuberance, we believe in a holistic approach to wellness. Beyond addressing your immediate symptoms, we strive to enhance your overall health and wellness through lifestyle recommendations, nutritional guidance, and exercise plans.
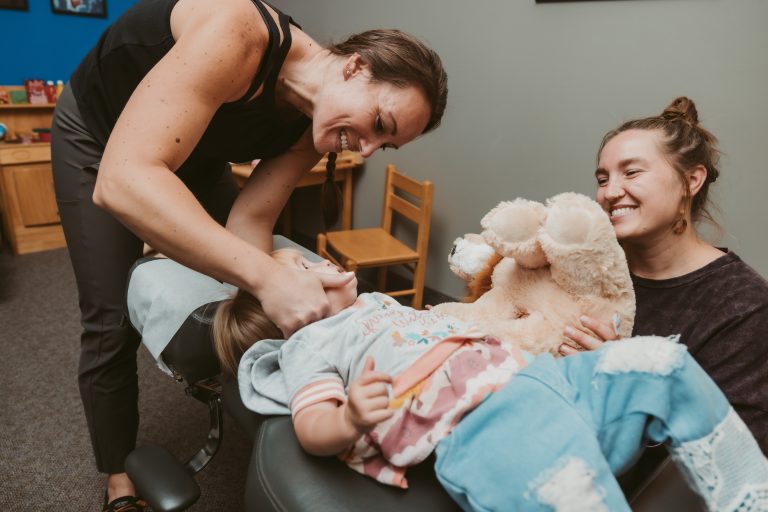
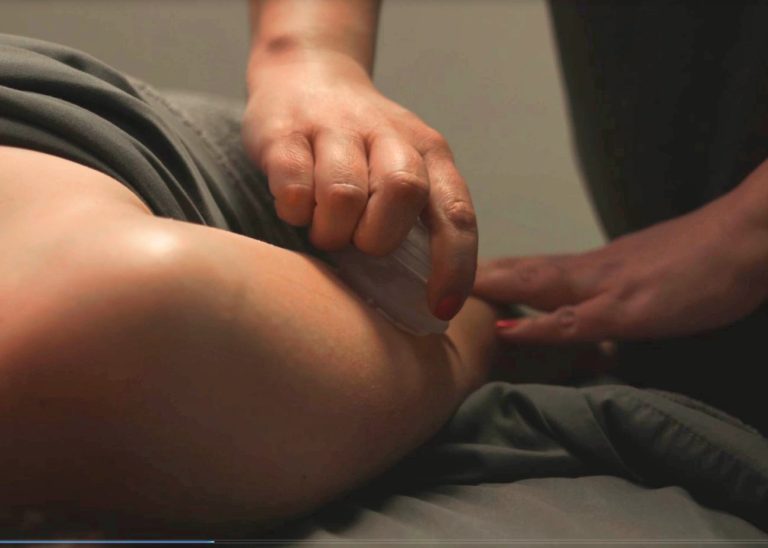
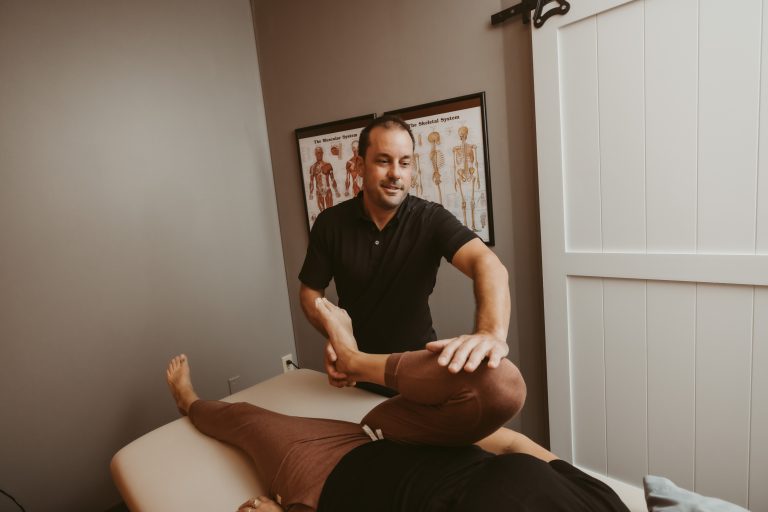
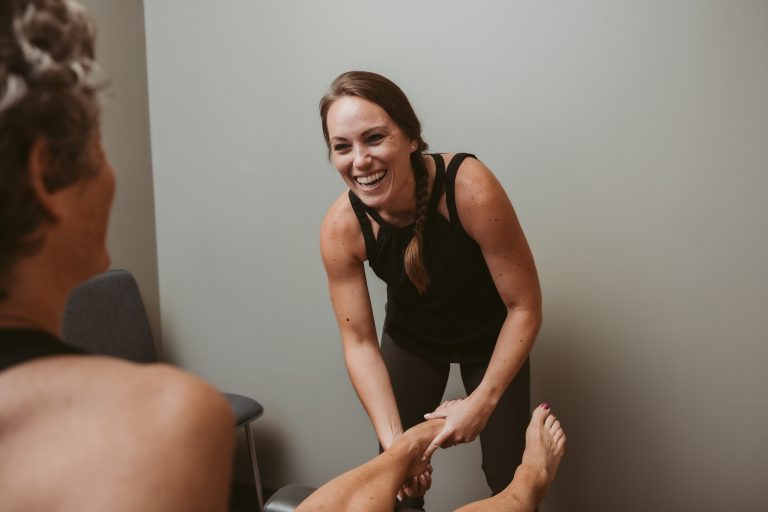






Whether you are seeking relief from pain, recovering from an injury, or simply want to optimize your health, Exuberance is here for you. Our team is passionate about helping you achieve your health and wellness goals, so you can embrace life with vitality and exuberance.

Insurance Providers
Most Insurance Providers Accepted
View AllAddress
17830 Kenwood Trail
Lakeville MN 55044
Lakeville MN 55044